Investigating dendritic cell maturation in dendritic cell progenitors
Robrecht Cannoodt
2016-01-22
Source:vignettes/ginhoux.Rmd
ginhoux.RmdIn this vignette, SCORPIUS is used to infer a trajectory through
dendritic cell progenitors. The ginhoux dataset contains
248 dendritic cell progenitors in one of three cellular cellular states:
MDP, CDP or PreDC.
The dataset is a list containing a matrix named
expression and a data frame named
sample_info.
expression was a 245-by-15752 matrix containing the
expression values of all the cells and all the genes, but this dataset
had to be reduced to 2000 genes in order to reduce the package size. See
?ginhoux for more info.
ginhoux$expression[1:6, 1:6]## Mpo DQ688647 Ly6d Snora31 Prtn3 DQ567485
## SRR1558744 1.6168843 9.041883 1.616884 10.587718 8.342093 9.349044
## SRR1558745 8.6334859 11.435542 0.000000 7.931509 9.217237 10.047680
## SRR1558746 0.0000000 11.056615 0.000000 0.000000 9.495118 9.532252
## SRR1558747 0.9744123 11.962396 12.902384 0.000000 0.000000 10.954714
## SRR1558748 10.0596172 11.035344 0.000000 0.000000 9.371665 10.211225
## SRR1558749 8.7327325 7.612738 0.000000 7.986711 9.863754 8.009253sample_info is a data frame with the metadata of the
cells, containing cell types of the individual cells.
head(ginhoux$sample_info)## group_name
## SRR1558744 CDP
## SRR1558745 CDP
## SRR1558746 CDP
## SRR1558747 CDP
## SRR1558748 CDP
## SRR1558749 CDPIn order to infer a trajectory through this data, SCORPIUS first reduces the dimensionality of the dataset.
Reduce dimensionality of the dataset
SCORPIUS uses Torgerson multi-dimensional scaling to reduce the dataset to three dimensions. This technique attempts to place the cells in a space such that the distance between any two points in that space approximates the original distance between the two cells as well as possible.
The distance between any two samples is defined as their correlation
distance, namely 1 - (cor(x, y)+1)/2. The reduced space is
constructed as follows:
expression <- ginhoux$expression
group_name <- ginhoux$sample_info$group_name
space <- reduce_dimensionality(expression, "spearman", ndim = 3)The new space is a 245-by-3 matrix, and can be visualised with or without colouring of the different cell types.
draw_trajectory_plot(space, progression_group = group_name, contour = TRUE)## Warning: `aes_string()` was deprecated in ggplot2 3.0.0.
## ℹ Please use tidy evaluation idioms with `aes()`.
## ℹ See also `vignette("ggplot2-in-packages")` for more information.
## ℹ The deprecated feature was likely used in the SCORPIUS package.
## Please report the issue at <https://github.com/rcannood/SCORPIUS/issues>.
## This warning is displayed once every 8 hours.
## Call `lifecycle::last_lifecycle_warnings()` to see where this warning was
## generated.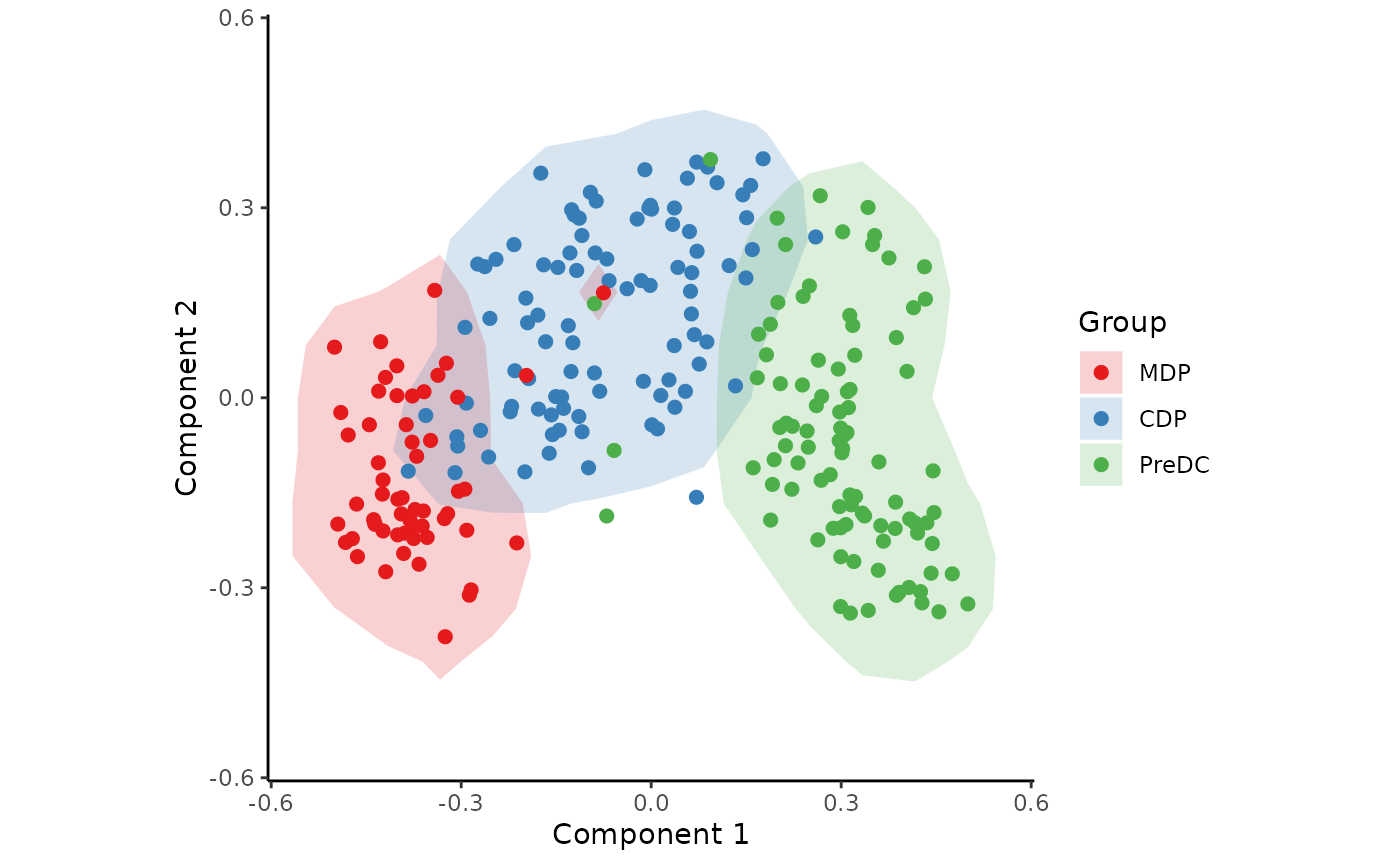
Inferring a trajectory through the cells
The main goal of SCORPIUS is to infer a trajectory through the cells, and orden the cells according to the inferred timeline.
SCORPIUS infers a trajectory through several intermediate steps, which are all executed as follows:
traj <- infer_trajectory(space)The result is a list containing the final trajectory
path and the inferred timeline for each sample
time.
The trajectory can be visualised with respect to the samples by
passing it to draw_trajectory_plot:
draw_trajectory_plot(
space,
progression_group = group_name,
path = traj$path,
contour = TRUE
)## Warning: Using `size` aesthetic for lines was deprecated in ggplot2 3.4.0.
## ℹ Please use `linewidth` instead.
## ℹ The deprecated feature was likely used in the SCORPIUS package.
## Please report the issue at <https://github.com/rcannood/SCORPIUS/issues>.
## This warning is displayed once every 8 hours.
## Call `lifecycle::last_lifecycle_warnings()` to see where this warning was
## generated.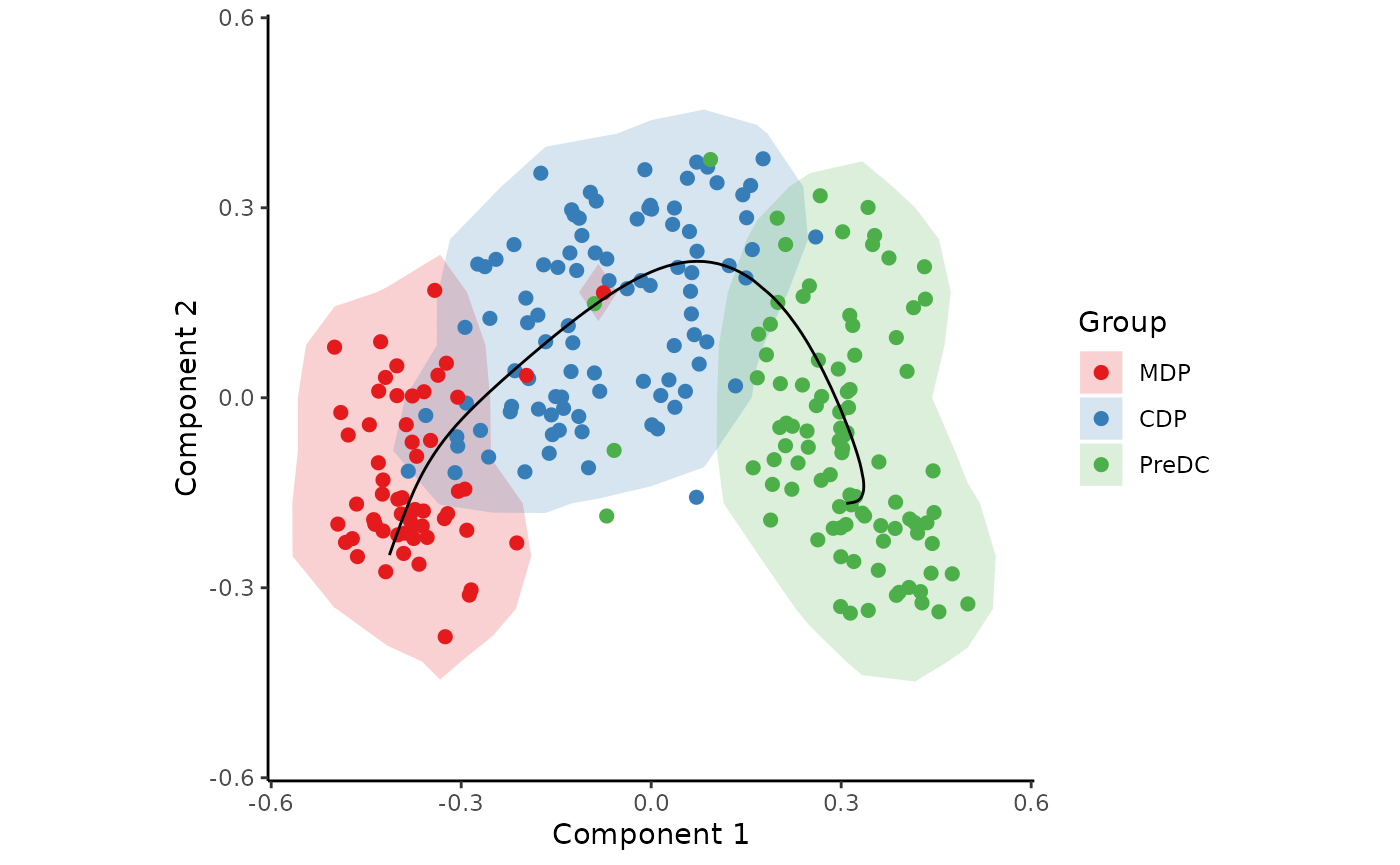
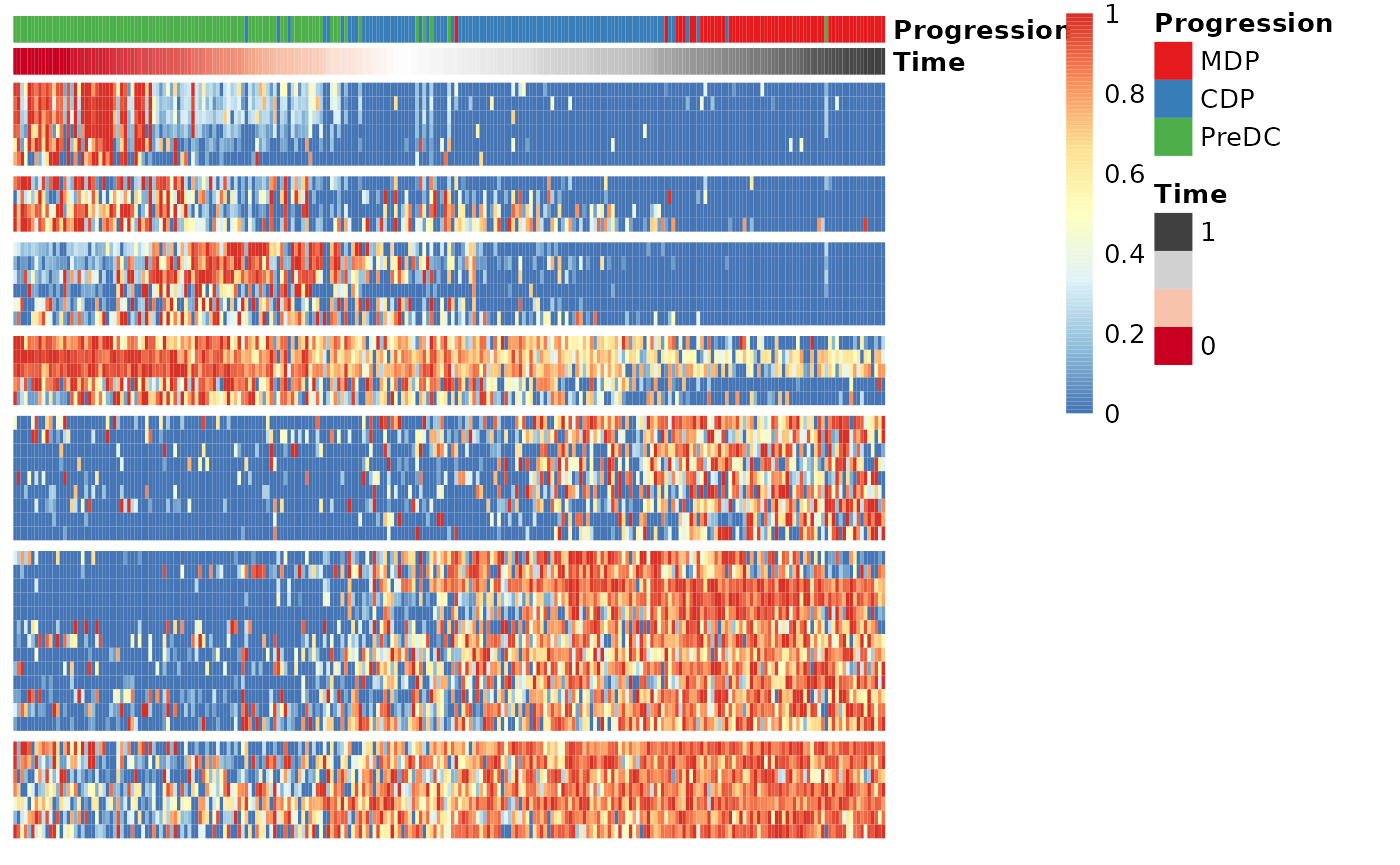
Finding candidate marker genes
We search for genes whose expression is seems to be a function of the trajectory timeline that was inferred, as such genes might be good candidate marker genes for dendritic cell maturation.
gimp <- gene_importances(expression, traj$time, num_permutations = 0, num_threads = 8)
gene_sel <- gimp[1:50,]
expr_sel <- expression[,gene_sel$gene]To visualise the expression of the selected genes, use the
draw_trajectory_heatmap function.
draw_trajectory_heatmap(expr_sel, traj$time, group_name)
Finally, these genes can also be grouped into modules as follows:
modules <- extract_modules(scale_quantile(expr_sel), traj$time, verbose = FALSE)
draw_trajectory_heatmap(expr_sel, traj$time, group_name, modules)